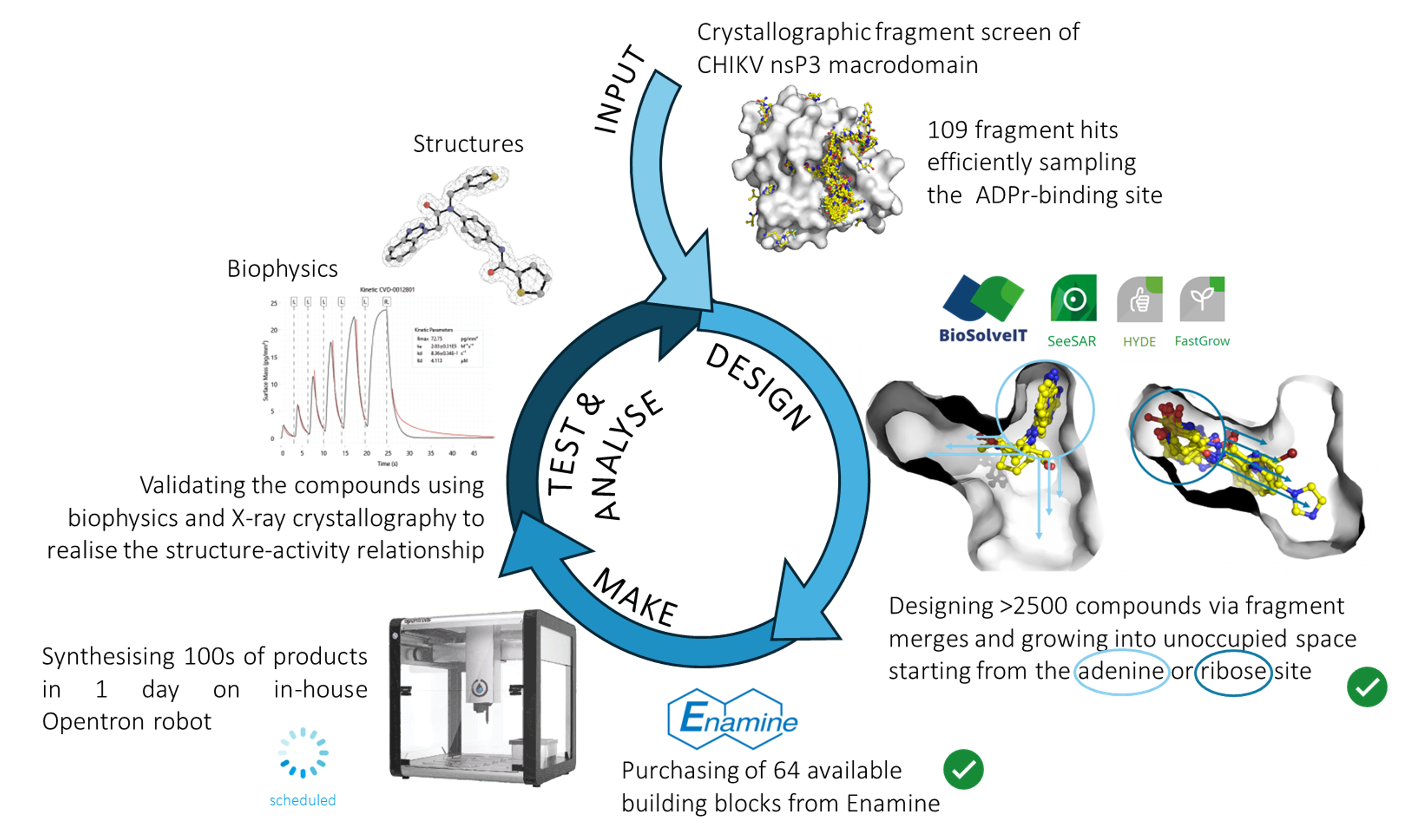
In the last three months, we used the granted license from BioSolveIT to design >2500 new compounds for the CHIKV nsP3 macrodomain. As we had some preliminary data on fragment merges/follow-up compounds that could be easily synthesised via amidation reactions on our in-house Opentron robotic system, we decided not to purchase the designed compounds directly, but rather the amine and acid building blocks. As only 64 of the 438 building blocks were available for purchase from Enamine at that time, we did not have to use HIPPO to down-sample. The 64 building blocks have arrived and the compounds are due to be synthesised in the next two months. In the meantime, we have established suitable amidation reaction conditions that will allow us to directly soak the crude reaction mixtures into the crystals for X-ray crystallographic analysis and have started to establish conditions for the GCI and ITC assays.
After 3 months, Jasmin Cara has achieved the following milestones:
- Using BioSolveIT, we designed compounds based on the previously obtained fragment screen hits or early validated algorithmic fragment merges that could be easily synthesised via amidation reactions on our in-house Opentron robot. We generated the compounds via fragment merging, linking or growing starting from two different sites: from the adenine site towards the oxyanion site or phosphate site (‘pyrrolopyrimidine series’); and from the ribose site towards the phosphate site and oxyanion site (‘sulfolane series’). This resulted in 1012 and 1548 potential scaffolds for the sulfolane and the pyrrolopyrimidine series, respectively, which would be generated from 438 building blocks (acids and amines). Unfortunately, due to availability, we were only able to purchase 64 of the building blocks, which will be used to synthesise ~100 pyrrolopyrimidine and ~150 sulfolane series compounds.
- The scaffolds have arrived and the compounds are due to be synthesised on our in-house Opentron robotic system end of June/early July. In the meantime, I have tested various solvents and coupling reagents used during amidations on the CHIKV nsP3 macrodomain crystal system, to ensure we can use the crude reaction mixtures from the Opentron synthesis directly for crystal soaking without affecting the crystal and, therefore, data quality during X-ray diffraction. Efforts to establish optimal conditions for the GCI and ITC assays are currently ongoing, as well.
- Not started yet.