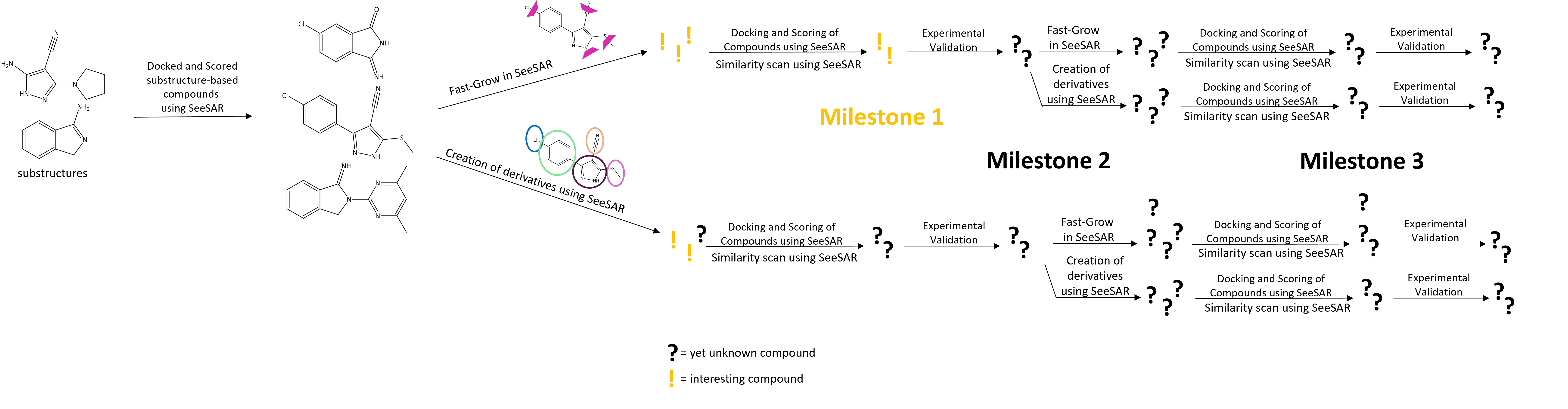
The development of the lead structures for the inhibition of the chaperone IpgC in Shigella based on three lead structures was started using SeeSARs Fast-grow libraries. Various molecules were obtained and docked. Afterwards, the molecules were scored in SeeSAR’s Analyzer Mode applying different criteria e.g. unstrained torsion angles, no molecular clashes, molecular weight and partition coefficient according to the rule of five. For the ligand binding in the natural interaction partner’s binding site many molecules with desired properties were received. These will be used in assays and X-ray crystallography experiments very soon once they are purchased/ synthesized. Based on the results they will be further developed in SeeSAR. For the other two lead structures no molecules with desired properties were obtained. They are binding in the dimer-interface of the IpgC-homodimer which impedes the fragment-growing. Using a monomer only did also not lead to molecules with desired properties.
After 3 months, Johanna has achieved the following milestones:
- The three lead structures were enlarged using SeeSAR Fast-grow via different single bonds in the molecules. Resulting molecules were docked by a standard- and a template-based docking using the lead structures, followed by scoring in the Analyzer Mode. Various criteria for scoring e.g. unstrained torsion angles and no molecular clashes were applied and SeeSAR’s intuitive colour code accelerated the process so that only molecules with the desired properties remained. Obtained molecules were then inspected visually in SeeSAR. For two of the three molecules unfortunately, no molecules are suitable for further investigation. For the third molecule though, which is the one binding in the natural interaction partner’s binding site, many molecules were received. The purchase/ synthesis will be undertaken soon. (For the third molecule it was interesting that upon pdb loading and ligand extraction a tautomer of the deposited molecule was shown which was then used for fragment-growing.)
- After purchase or synthesis of the molecules obtained with SeeSAR Fast-grow, which were docked and scored, they will be used in assays and X-ray crystallography experiments will be performed. Based on the results further development of the ligands will be undertaken in SeeSAR. Furthermore, the search and creation of derivatives for the two so-far-not-successful molecules have already started. These will be docked and scored as a next step.
- This milestone will be undertaken as soon as results from Milestone 2 are present.