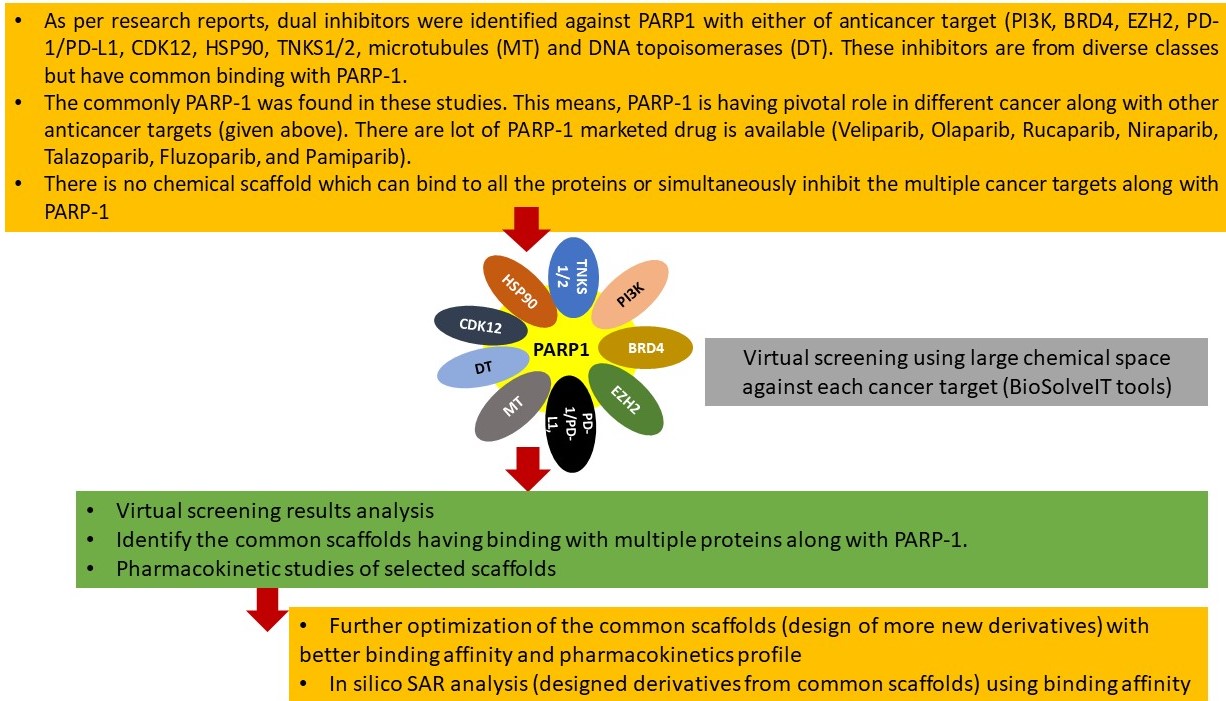
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1), a key enzyme in DNA repair, has emerged as a promising anticancer druggable target. There are different marketed drugs [Veliparib, Olaparib, Rucaparib, Niraparib, Talazoparib, Fluzoparib, and Pamiparib] available against PARP1 for the treatment of various cancers: cervical, colorectal, ovarian, prostate, breast and pancreatic cancer. Moreover, dual inhibitors were designed and tested against PARP1 along with different cancer targets till date like PI3K, BRD4, EZH2, PD-1/PD-L1, CDK12, HSP90, TNKS1/2, microtubules and DNA topoisomerases. Unfortunately, there are no common chemical scaffolds reported till date which can target to all these anti-cancer targets or multiple anti-cancer targets along with PARP-1. The aim of the studies is to identify the common scaffolds which can bind to multiple anti-cancer targets along with PARP-1.
Pawan intends to achieve the following milestones:
- Understanding the structural bioinformatics (sequence and structural similarity) of the different anti-cancer targets with PARP1
- Identification of common scaffolds which can bind to PARP1 as well as other cancer targets: PI3K, BRD4, EZH2, PD-1/PD-L1 , CDK12, HSP90, TN
- Optimization of the common scaffolds with better binding and pharmacokinetic parameters