Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) refers cancer cells that don’t express estrogen and progesterone receptors and human epidermal growth factor 2 (ER, PR and Her2). TNBC accounts for 10-15% of all breast cancer and categorized by reduced response, high rates of relapse and increased metastasizability. RSK2, a convergence node for both MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways.
In this study, we hypothesize that inhibition of down-stream RSK2 signaling holds the potential of blocking TNBC independently of the mutated upper-stream pathways.
Exploring possible binding sites (pockets) in the target protein RSK2
The binding sites of reported structures were analyzed using the webtools including (https://proteins.plus), The ligand-RSK2 (NTKD or CTKD) was scrutinized. Mode of binding and ligand-target interactions (LTIs) were closely analyzed enabled by SeeSAR's Analyzer, PyMol (Educational Use: https://pymol.org/ep/), and LigPlot+ v.2.2 - ligand-protein interaction diagrams (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/software/LigPlus/).
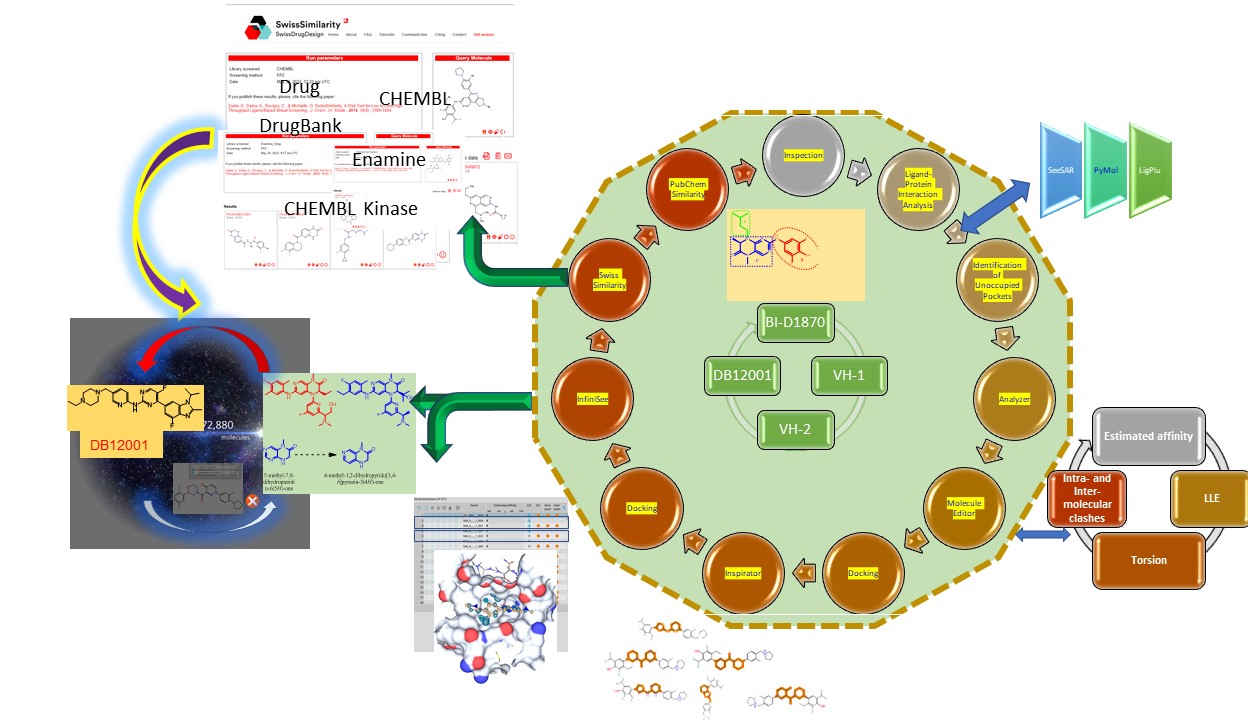
Briefly, an iterative cyclic workflow was adopted starting form Inspection, Analysis of Ligand-Protein Interaction, Identifying Unoccupied Pockets, Analyzer, Molecule Editor, Inspirator, Docking and InfiniSee was employed.
Hybrid Structure and Ligand-Based Virtual Design: In each case the ligand was selected for defining the amino acids encompassing the BS. Ligands were transferred to “Editor” and extensive sequential structural modifications were introduced manually, affinity was calculated. Derivatives with improved affinity were transferred to the docking mode. In a following step, “promising” ligands were selected for successive “ligand-based” Inspirator. Each VH was subjected “Inspirator”. The affinity of the Proposed “inspirited” moieties was estimated and synthons with good positioning in the binding pocket/s were selected for further ligand-based VS either by using InfiniSee or Swisssimilarity platforms.
Manual Construction of Virtual Hits: In the current venture we applied a Hybrid Structure and Ligand Based Drug Design approach (HSLBDD). BioSolveIT tools (SeeSAR and InfiniSee were intensively utilized. Besides, we got assisted by web-based tools and publicly available databases. VS using InfiniSee was performed on libraries that exceed 2.9X1016 molecules.
Pteridines are considered among privileged scaffolds highly abundant in chemical space and proved to be highly beneficial in contemporary lead generation platforms. In one case the main pteridine scaffold was retained (aside from converting the 7,8-dihydropteridin-6(5H)-one to 1,2-dihydropyrido[3,4-b]pyrazin-3(4H)-one). Modifications were introduced at the decorative substituents i.e. the 3,5-difluoro-4-hydroxyphenyl)amino and 3-methylbutyl group.
After 1 year, Yousef has achieved the following goals:
- While critical hydrogen bonds were conserved, and unoccupied pockets were visualized (SeeSar), sequential modifications were performed employing the “Editor”. The estimated affinity, LLE, Torsion, Intra- and Inter-molecular clashes were concurrently estimated. This iterative process was concluded in identifying few “Virtual Hits. VHs were used in ligand-based VS employing InfiniSee. Swisssimilarity was also exploited. In a further step, VH-1 was subjected to Inspirator. This was executed part-by-part: replacement of the core 1,2-dihydropyrido[3,4-b]pyrazin-3(4H)-one was followed by replacing 5-(difluoromethyl)-2-ethyl-3-fluoro-4-methylaniline and 1-(o-tolyl)pyrrolidine parts. Interestingly, several moieties were proposed as substitutes for the core 1,2-dihydropyrido[3,4-b]pyrazin-3(4H)-one. Among them were the 3-(morpholine-4-carbonyl)pyridazin-4(1H)-one, 2,5- disubstituted pyrazine [morpholino(pyrazin-2-yl)methanone] and others.
- Virtual Screening for Novel RSK2 Inhibitors with Druglike Properties: In an attempt to “virtually construct” novel derivatives, a small library of compounds coined “COMBs” was created. The compounds were drawn on ChemDraw, transformed into “sdf” format and docked into the binding site of BI-D1870 [(7R)-2-[(3,5-difluoro-4-hydroxyphenyl)amino]-5,7-dimethyl-8-(3-methylbutyl)-7,8-dihydropteridin-6(5H)-on, 584]. Interestingly, some of those virtual constructs dock nicely into the binding site with the 2,5-difluorophenyl residing at the interior hydrophobic pocket that accommodated 3,5-difluoro-4-hydroxyphenyl in 584. Docking showed that morpholine-4-carbonyl)-1-pyridazin-4(1H)-one moiety spanns over the binding region of 8-dihydropteridin-6(5H)-one and connects the -(3-methyl-4-(pyrrolidin-1-yl) and derivative morpholine-4-carbonyl)-1phenyl)pyridazin-4(1H)-one.
- Repetition (in sequence and parallel manners) of the workflow depicted in the figure below was concluded in identifying simpler potential VHs. This effort was concluded in identifying two SBVHs and two HSLBVHs. One of the VHs identified employing the hybrid approach was Abemaciclib (Verzenio), a CDK 4/6 inhibitor approved for treating advanced or metastatic breast cancer and proved to be growth and spread of cancer cells in the body. This workflow was adopted in derivatizing additional RSK2 NTKD reported inhibitors [like: 4NW6 and 4NW5, 4GUE, 4EL9, etc.] Currently, we are focusing of portraying synthetic procedures for optimal preparation of VHs. A retrosynthesis analysis was performed to find commercially available building blocks and reagent. In addition, additional computational exertion that aims at distinguishing druglike RSK2 inhibitors is planned down the road. Arranging for financial resources one main challenge we are devoting efforts to.