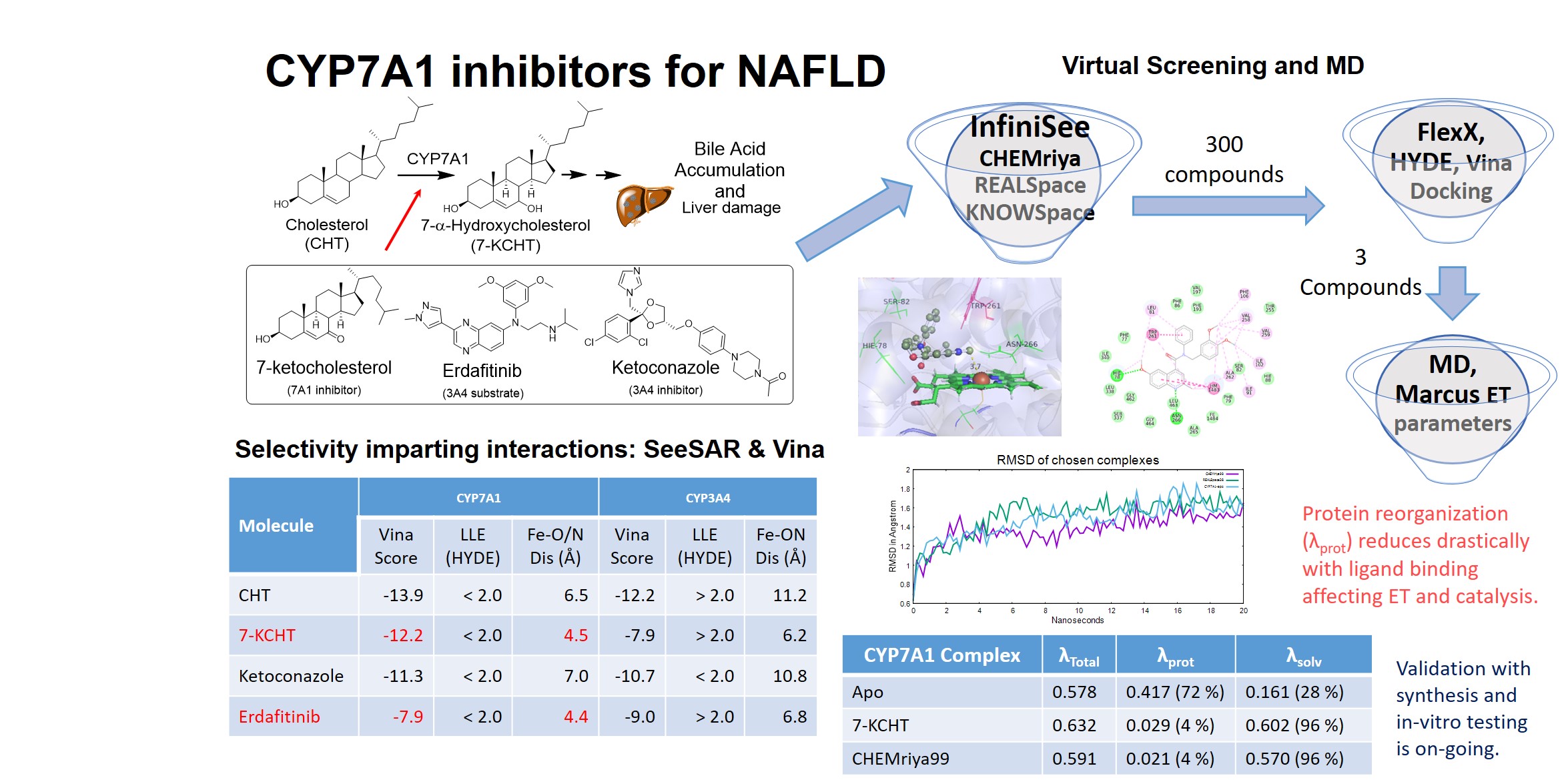
NAFLD has emerged as a silent killer complicating the treatment of metabolic and cardiovascular disorders. Bile acid (BA) accumulation in NAFLD triggers liver damage, NASH and liver failure. Strategies indirectly inhibiting BA synthesis via FXR agonists and bile acid analogues have been unsuccessful in clinical trials. Thus we targeted CYP7A1 to inhibit the rate-limiting step in BA biosynthesis. Since Medicinal Chemistry of CYP7A1 ligands is uncharted, we chose 3A4 and 7A1 inhibitors/substrates (Erdafitinib, Ketoconazole, and Cholesterol, 7-ketocholesterol respectively) to study protein-ligand interactions. InfiniSee search interestingly returned quinolines, which were docked using SeeSAR (FlexX) and AutoDock Vina. A distance and affinity (Hyde/Vina score) based filter returned similar compounds (TC; 0.5-0.8). Marcus electron transfer (ET) parameters from MD analysis gave insights into isoform specificity. Synthesis and spectroelectrochemical analysis is under progress.
After 3 months, Vaibhav has achieved the following milestones:
- Four compounds (Cholesterol, 7-ketocholesterol, Ketoconazole and Erdafitinib) were docked using FlexX in SeeSAR and AutoDock Vina using in-house python scripts. For Vina docking AMBER charges and radii were assigned to porphyrin and Fe atoms. Since Type II CYP450 inhibitors are known to form close contacts with the Heme atom, a distance and higher vina score criteria was chosen. For FlexX docking a similar distance, higher LLE and absence of repulsive interactions were considered as the desired characteristics of potential inhibitors. 7-ketocholesterol and Erdafitinib showed similar interactions with TRP261, SER82 in the CYP7A1 active site. While in CYP3A4, cation-pi interaction with ARG187 prevented a close approach to the Heme centre. This analysis showed that Erdafitinib like compounds are likely to be selective for CYP7A1. Thus Erdafitinib was used in InfiniSee for virtual screening.
- Virtual screening with InfiniSee using three libraries (CHEMriya, KnowledgeSpace, RealSpace) and Erdafitinib as a template gave 300 potential inhibitors. These were docked in SeeSAR (FlexX) and AutoDock Vina. A similar distance, LLE, quality of torsion, inter and intramolecular interactions and Vina Score based criteria were used to select potential inhibitors for MD simulations. Closer inspection of the structures and similarity showed that, unlike Erdafitinib, ortho-dimethoxy substituted quinolines bind preferably to the CYP7A1 with closer Heme contacts. The top 3 compounds identified in SeeSAR and Vina showed good similarity (TC: 0.5 – 0.8). Thus these compounds were chosen for MD simulations to access the impact of inhibitor binding on ET parameters.
- MD study for the chosen compounds was performed with AMBER18. An in-house script was used to prepare ligand PDB, perform parameterization of compounds in the antechamber and prepare Leap input files. Heme parameterization was performed with the MCBP.py tool. Twenty nanosecond MD simulations were performed for the apo and three potential inhibitor complexes. Trajectory analysis and post-processing (cpptraj and sander) allowed the estimation of vertical energy gaps and Marcus ET parameters (protein and solvent reorganization energies). The apo CYP7A1 reorganized substantially mostly due to active site collapse in the absence of a ligand. Whereas in the presence of potential inhibitors, solvent reorganization dominates and protein motions are relatively stabilized. The full impact of these structural movements is being analyzed further and will be validated by synthesis and in-vitro testing of these compounds.