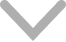
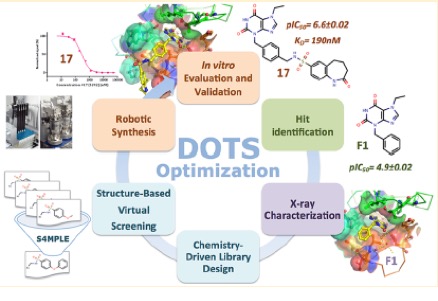
In recent decades, the identification of hits has been greatly facilitated by advances in high throughput screening (HTS) and the design of chemical libraries. It would be wishful to optimize the automation of the ‘hit-to-lead’ (H2L) process. Xavier will present an integrated strategy for the H2L optimization phase and the automated design of chemical probes called Diversity Oriented Target-Focused Synthesis (DOTS and CovaDOTS) approach.
In the ‘DOTS’ approach, a focused virtual library is generated by combining an activated fragment — corresponding to a substructure that binds to a target — with a collection of functionalized chemical blocks, using in silico encoded relevant chemical reactions. Target-specific compounds are selected by virtual screening, followed by in vitro synthesis and evaluation using a robotic platform. The proof of concept was successfully completed by the optimization of bromodomain inhibitors that lead to the validation of several compounds with an affinity that had improved by several orders of magnitude. The proposed process can be implemented in academic environments or biotechnology companies that desire an automation of these processes.
Register and tune in for a very exciting webinar.
1 Hoffer L. et al. J. Med. Chem. 2018 Jul 12;61(13):5719-5732; Carrasco K. et al., J. Med. Chem. 2022 Apr 14;65(7):5660-5674
2 Hoffer L., et al. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019 2019 Apr 22;59(4):1472-1485